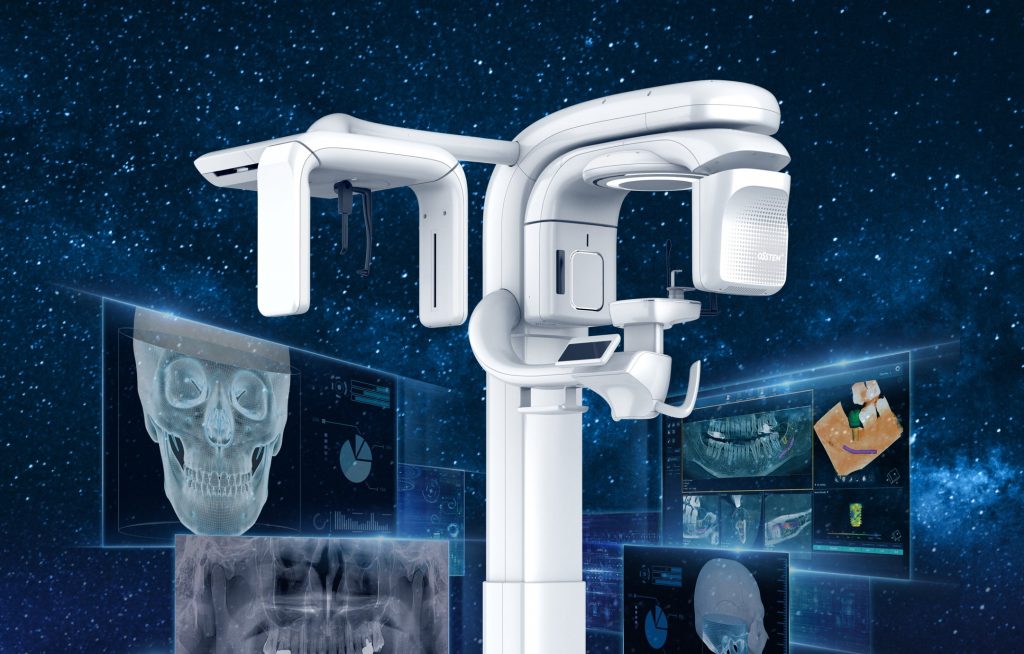
A dental CT (computed tomography) scan, also known as a cone beam CT (CBCT) scan, is an advanced imaging technique used to create highly detailed 3D images of a patient’s teeth, jaw, and surrounding structures. Unlike traditional X-rays, which provide a two-dimensional view, a dental CT scan offers a comprehensive 3D perspective, enabling precise analysis of the dental anatomy.
Key Uses of a Dental CT Scan:
- Implant Planning: The 3D images allow for accurate mapping of bone density and nerve locations, essential for safely placing dental implants.
- Orthodontics: It helps in assessing tooth position and jaw alignment, which is valuable for creating effective orthodontic treatment plans.
- Endodontics: Used for root canal treatments, a CT scan can detect complex root structures, hidden canals, and infections.
- Diagnosis of Pathologies: CT scans aid in diagnosing cysts, tumors, and other abnormalities in the jaw and facial bones.
- Trauma Assessment: In cases of facial injury, a CT scan can reveal fractures or other damage that may not be visible on regular X-rays.
Advantages of Dental CT Scans:
- High Resolution and Precision: Provides detailed images, capturing bone structures, soft tissue, and nerves with precision.
- Non-Invasive: The scan is quick and non-invasive, usually taking just a few seconds while the patient remains seated.
- Lower Radiation: CBCT scans use a lower radiation dose compared to traditional CT scans, making them safer for patients.
- Efficient Treatment Planning: With 3D imaging, dentists can plan treatments with greater accuracy, reducing the risk of complications.
Dental CT scans are highly valuable in complex cases and for procedures that require precise measurements, such as implant placement. By offering a comprehensive view of the dental anatomy, CT scans enhance diagnostic accuracy and allow for better patient outcomes.